Spinal Tuberculosis
Understanding Pott's Disease: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
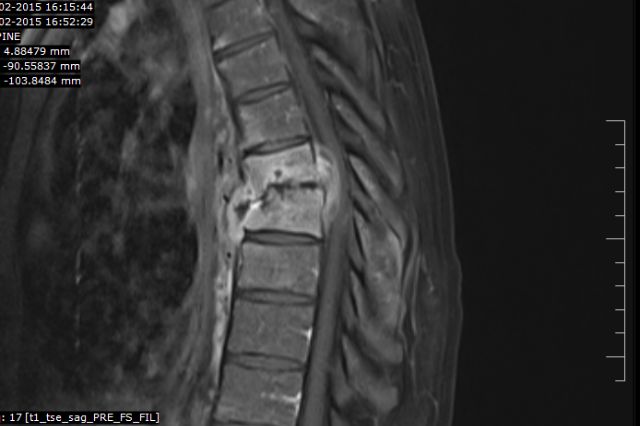
Tuberculosis (TB) is often associated with lung infections, but it can affect various parts of the body. One of the less-known but critically important forms is Spinal Tuberculosis, also known as Pott's disease.
Spinal tuberculosis primarily affects the vertebrae. It is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which spreads to the spine through the bloodstream. Once it reaches the spine, it can lead to the formation of abscesses and vertebral destruction, potentially compromising the spinal cord.
Symptoms to Watch For
Spinal TB can be insidious, developing slowly over time. Common signs include:
Diagnosis and Detection
Early diagnosis is crucial. Doctors typically use a combination of methods:
- Imaging: MRI is the gold standard for detecting early spinal changes, abscesses, and cord compression. X-rays and CT scans are also used.
- Biopsy: A sample of the affected tissue helps confirm the presence of bacteria.
- Blood Tests: ESR and CRP levels are usually elevated, indicating infection.
Treatment and Management
The good news is that Spinal Tuberculosis is highly treatable, though it requires patience.
1. Antibiotic Therapy
This is the cornerstone of treatment. A regimen of multiple antibiotics is taken for 9 to 18 months to ensure the bacteria is completely eradicated.
2. Surgical Intervention
Surgery is not always needed. It is reserved for cases with severe spinal deformity, large abscesses, or significant neurological deficits (weakness in legs).
3. Rest & Bracing
Bed rest and spinal braces may be used in the early stages to prevent deformity and reduce pain while the medications take effect.